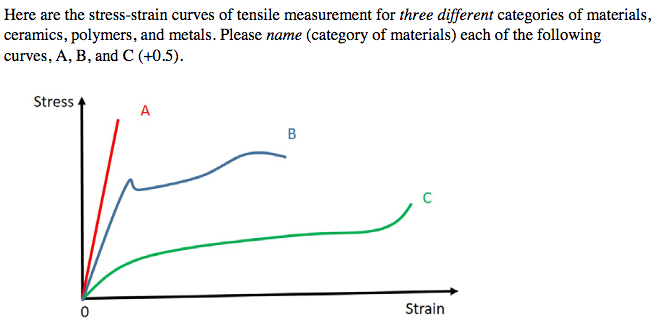
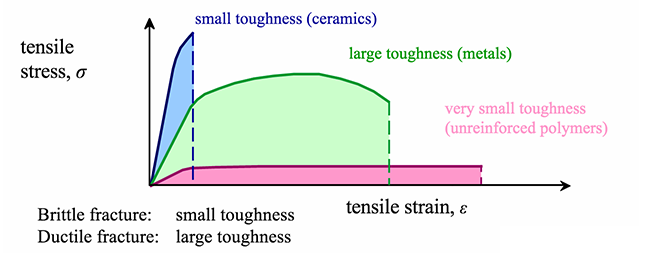
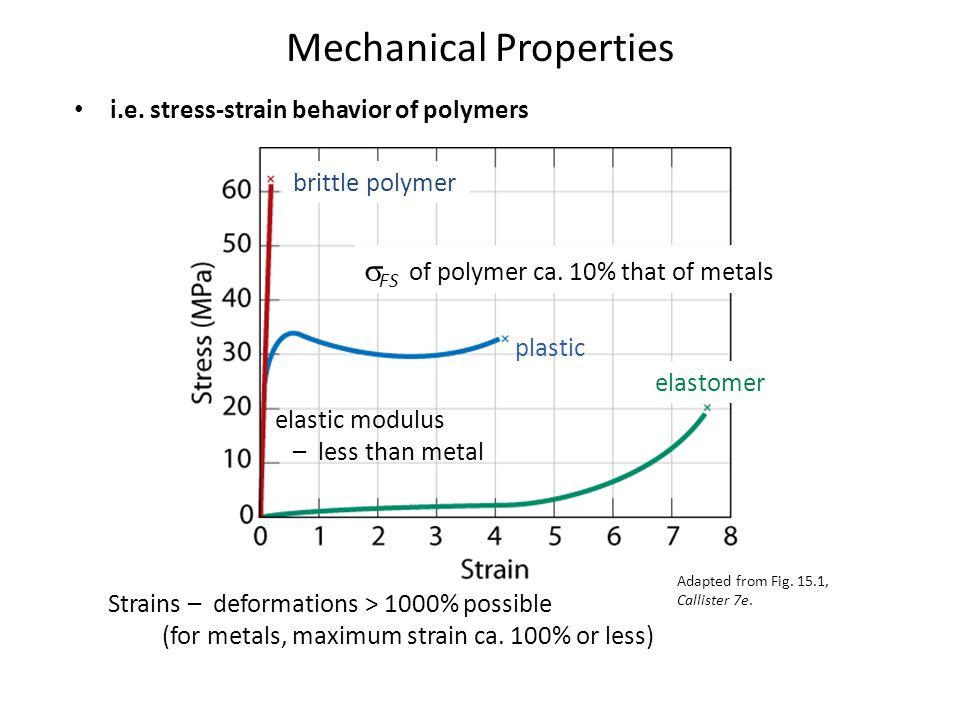
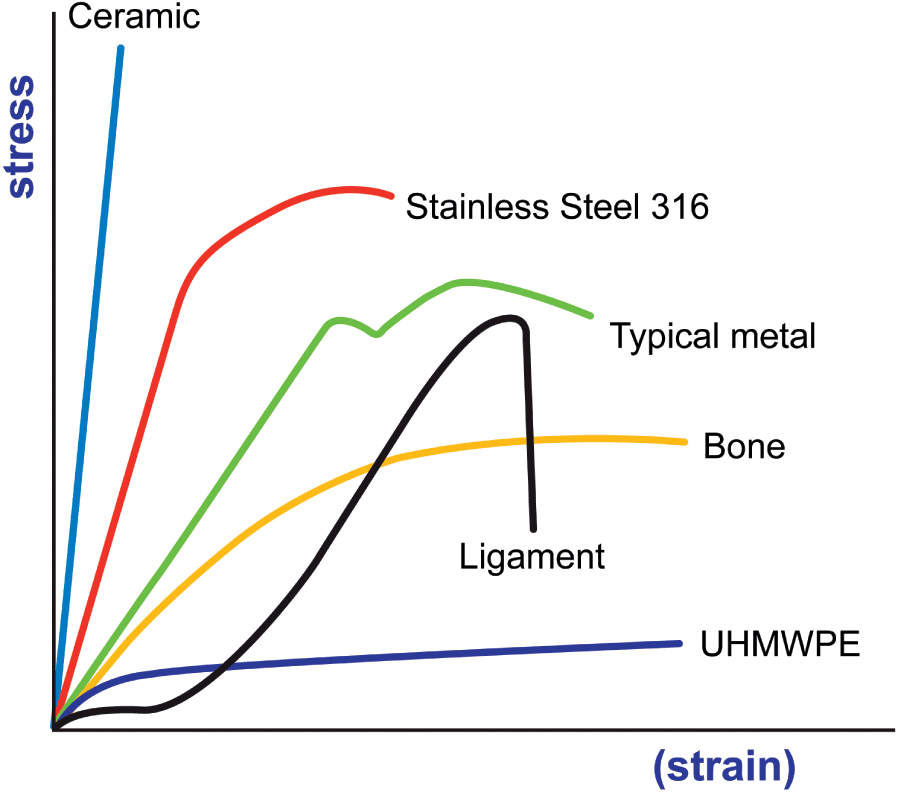
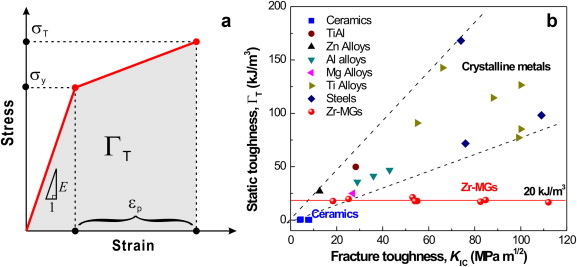
Another way at looking at resistance to failure for ceramic materials is to examine the energy required to drive cracks through the system.
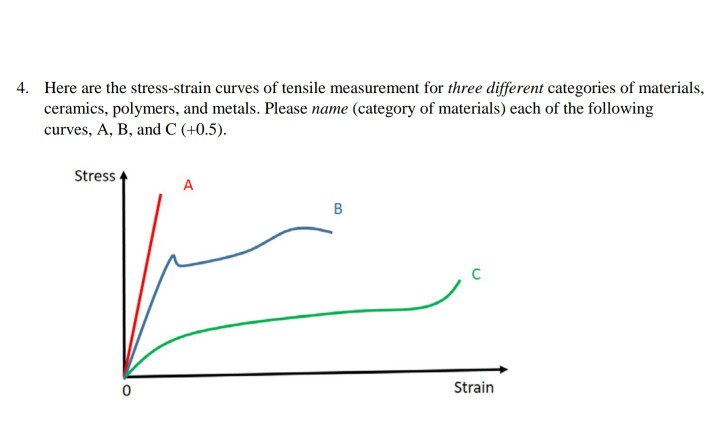
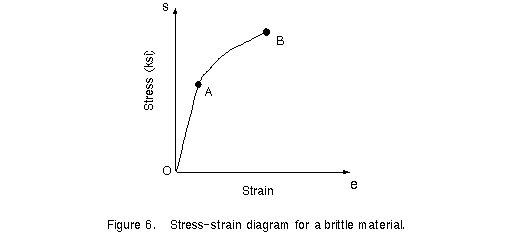
Stress strain curve of ceramic materials.
Generally a ceramic with more defects is weaker.
For brittle ceramics a three point bending apparatus shown in the figure below is used determine the stress strain behavior and the measurement results are used to calculate an equivalent modulus of elasticity.
It represents the maximum stress that a material can take before it fails.
After this point the curve starts dropping.
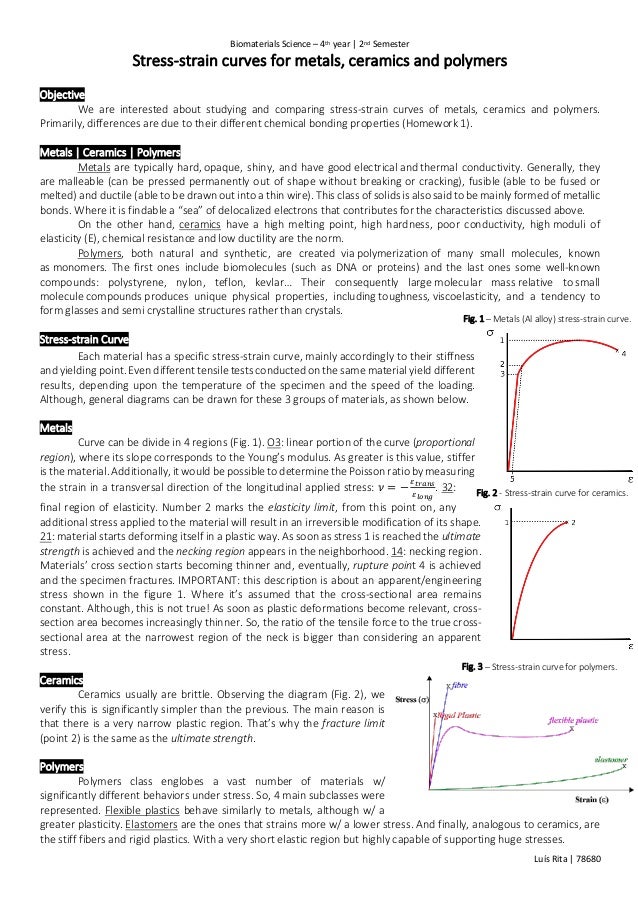
2 stress strain curve for ceramics.
The straight line implies that stress and strain share a linear or direct relationship throughout oa.
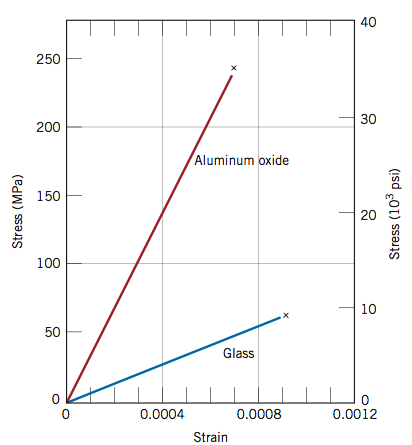
Stress strain curves for two brittle materials.
Click the resistance to fracture or area under the stress strain curve is the called the toughness.
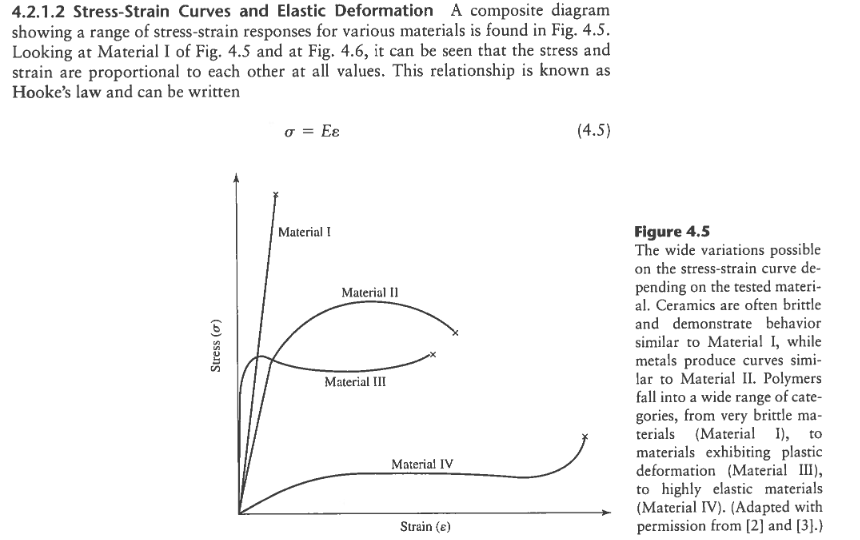
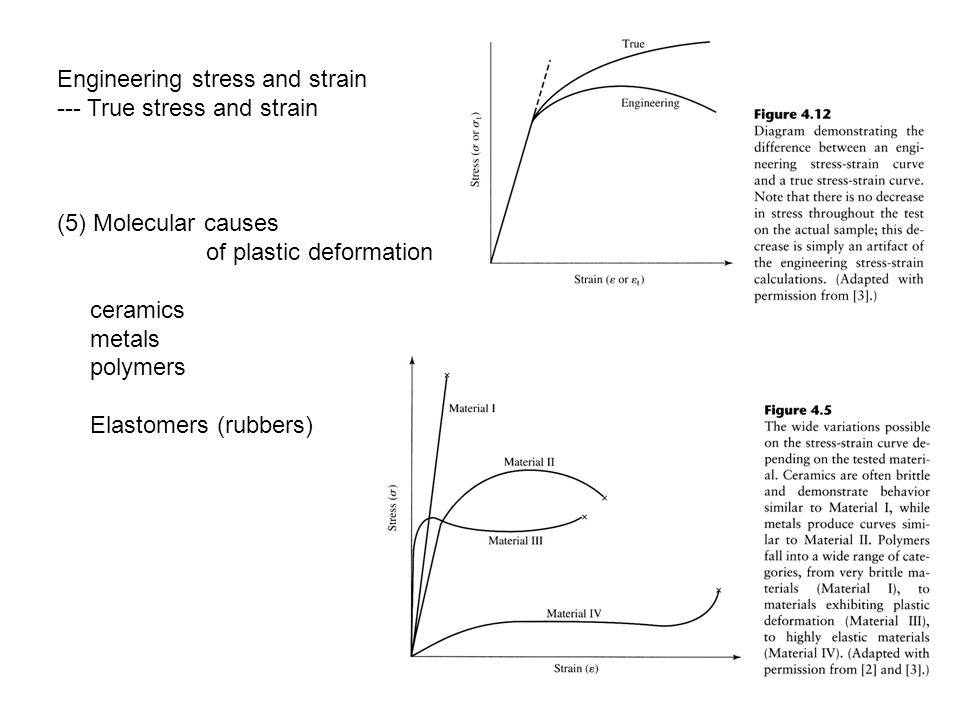
While some of the stress strain curves for polymers might look similar to ones for metals polymers are mechanically different than metals or ceramics.
This is shown by the point e on the graph.
Elastomers are the ones that strains more w a lower stress.
And finally analogous to ceramics are the stiff fibers and rigid plastics.
With a very short elastic region but highly capable of supporting huge stresses.
Where σ is the value of stress e is the elastic modulus of the material s ty is the tensile yield strength of the material and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which.
1 metals al alloy stress strain curve.
Stress strain curve is the plot of stress and strain of a material or metal on the graph.
A highly elastic polymer may stretch over 10 times the original length before breaking while a metal might elastically stretch 10 of the original length elastically and may stretch.
When a ductile material such as copper or aluminum is put under stress initially the resulting strain is proportional to the magnitude of the forces.
After plotting the stress and its corresponding strain on the graph we get a curve and this curve is called stress strain curve or stress strain diagram.
In materials science fracture toughness is the critical stress intensity factor of a sharp crack where propagation of the crack suddenly becomes rapid and unlimited.
The specimen however does not fail at this point.
We discussed this earlier.
This is depicted by the straight line oa.
Plane strain conditions give the lowest.
The material now is said to be plastic and the deformation is of nearly permanent nature.
In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain it is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing these curves reveal many of the properties of a material such as the young s modulus the yield strength.