A typical stress strain curve would look like figure 6 2strain curve.
Stress strain curve of metals ceramics and polymers.
Metallic bonding is great for this sort of re bonding which is why metals are usually ductile.
The yield point is the maximum of the stress strain curve the weird circle symbol.
The linear portion of the curve is the elastic region and the slope is the modulus of elasticity or young s modulus.
Elasticity ductility and tensile strength those four materials can be simplified by these definitions.
While some of the stress strain curves for polymers might look similar to ones for metals polymers are mechanically different than metals or ceramics.
A highly elastic polymer may stretch over 10 times the original length before breaking while a metal might elastically stretch 10 of the original length elastically and may stretch plastically to double the original length before reaching its fracture point.
In this the stress is plotted on the y axis and its corresponding strain on the x axis.
Low carbon steel generally exhibits a very linear stress strain relationship up to a well defined yield point fig 1.
For brittle ceramics a three point bending apparatus shown in the figure below is used determine the stress strain behavior and the measurement results are used to calculate an equivalent modulus of elasticity.
Stress strain curves for two brittle materials.
Elastic energy ductile fracture.
Plasticity happens when the atoms slip when they break bonds and reform new ones.
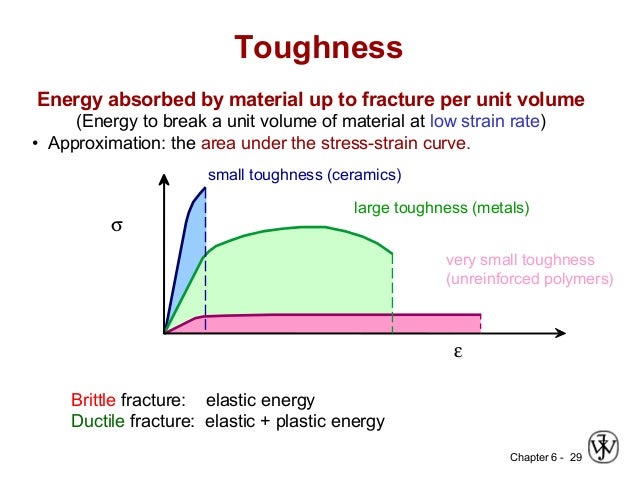
Elastic plastic energy very small toughness unreinforced polymers engineering tensile strain ε engineering tensile stress σ small toughness ceramics large toughness metals adapted from fig.
Primarily differences are due to their different chemical bonding properties homework 1.
Approximate by the area under the stress strain curve brittle fracture.
In reality not all stress strain curves perfectly resemble the one shown in strain figure 6 2.
The stress shown in is an example of a textfigure 6 2 book stress strain curve.
Stress strain curve is the plot of stress and strain of a material or metal on the graph.
Based on the mentioned properties.
Many ductile materials including some metals polymers and ceramics exhibit a yield point.
This stress curve is typical for ductile metallic elements.
It makes them dense and eventuall.
Metals and its alloys contain atoms that are arranged in orderly manner.
Difference between metals ceramics and polymers with respect to modulus and tensile strengths the modulus values for highly elastic polymeric materials are lower than those of metals.